At the RAK Research and Innovation Center at American University of Ras in United Arab Emirates (UAE), a group evaluated two tubular daylighting devices (TDD) in an attempt to find a solution that would provide excellent illumination along with energy efficiency and that would not contribute to health problems, ecological damage or pollution that is caused by other lighting technologies.
The UAE receives over 10 hours of daily sunlight on average and has about 350 sunny days each year, making it an excellent region to evaluate and implement daylighting solutions that use the sun as the illuminating source. TDDs operate on the principle of light reflection. As the light rays hit the roof, a dome that is located on the roof collects the ray and reflects it inside of a reflective mirror surface inside the light tube. The ray is then transferred into the building through a diffuser that spreads the light evenly. The TDDs collect both direct and diffuse light beams and reflect them into the room. The challenge in designing the TDDs is to find the best ratio of the diffuse and direct beam light. On a sunny day, TDDS have the advantage of providing excellent illuminance values. On the other hand, illuminance values can rise and fall based on the weather.
To study the two types of TDDs from different manufacturers, Solatube and Sun-Dome, the researchers installed two identical rooms.

One was equipped with a 21-inch TDD from one manufacture while the other has four 13-inch TDDs from another manufacturer. They performed illuminance measurement using a Hera spectrometer from Admesy, which helped show how well—in terms of both illuminance and chromaticity--the TDDs transfer the light into interiors throughout the day.
Findings
The researchers found that the intensity results for the two rooms were different. They found that the illuminance values for room 1 were more stable, while the curve of room 2 has many fluctuations.
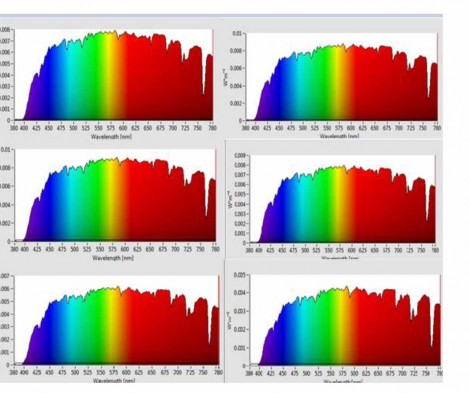
The average illuminance value for room 1 during that period was 412. 24 lux.
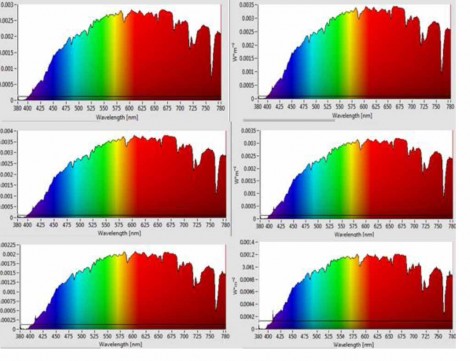
For room 2 the average illuminance for the same period was about 111. 76 lux during.
They were able to obtain illuminance values on both sunny and cloudy days. They also obtained color temperature values (CCT) for both rooms as well as spectral values (CRI). They concluded that because they found differences in the illuminance values in each, that the quality of the light issued from a TDD technology depends on the manufacturer and could be different from one manufacturer to another. One of the disadvantages that they found with TDD technology is the varying light levels during a cloudy day. One advantage of the TDD technology was the CRI values which were high throughout the days that the tests were performed.
Overall they concluded that daylighting technology can be useful in the UAE region. Although they performed their measurement in December, which is fall in the UAE and the sun is not at its highest, the lux levels were acceptable. With that understanding, spring and summer illumination results would be even higher.
Written by Omar Akash, Zaki Iqbal, Mousa Mohsen RAK Research and Innovation Center, American University of Ras Al Khaimah, Ras Al Khaimah, with editing by Anne Fischer, Managing Editor, Novus Light Technologies Today
For more information, read “Evaluation of To Different Tubular Daylighting Devices in UAE Climate”.


















 Back to Enlightening Applications
Back to Enlightening Applications